研究開発におけるマルチフィジックスシミュレーションの具体例
さまざまな業界のエンジニア, 研究者, 科学者がマルチフィジックスシミュレーションを使用して革新的な製品の設計とプロセスを研究および開発しています. COMSOL カンファレンスで発表したテクニカルペーパーやプレゼンテーションからインスピレーションを得てください. 以下の選択項目を参照するか, クイック検索ツールを使用して特定のプレゼンテーションを検索するか, アプリケーション領域でフィルタリングします.
COMSOL コンファレンス 2020 論文集を見る
A Black-Oil Model for Primary and Secondary Oil-Recovery in Stratified Petroleum Reservoirs
Black-oil simulators are commonly used in petroleum reservoir engineering for the prediction of oil production, especially during the earlier stages of oil-field exploitation, while also serving to guide pressure maintenance strategies in the longer term. Such models account for fluid ... 詳細を見る
Model and App of Hydrophobic Meshes Used in Oil Spill Recovery
Hydrophobic meshes are a new, promising technique for the recovery of spilled oil in the ocean. They allow to recover and store oil, while filtering it from the surrounding water. They are clean, efficient and can be used in continuously. These meshes have one drawback, however: if they ... 詳細を見る
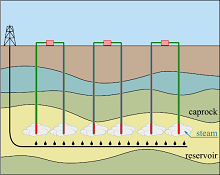
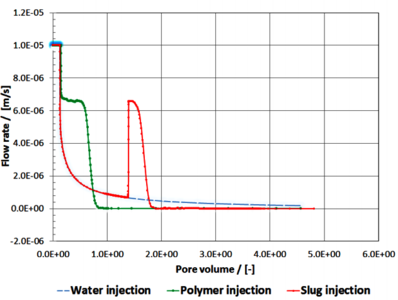
Development of COMSOL-Based Applications for Heavy Oil Reservoir Modeling
The efficiency and environmental impact of oil production become a principal challenge of energy producing companies. The improvement of existing and development of novel methods are often feasible within either a “new” physical framework (from the viewpoint of oil reservoir ... 詳細を見る
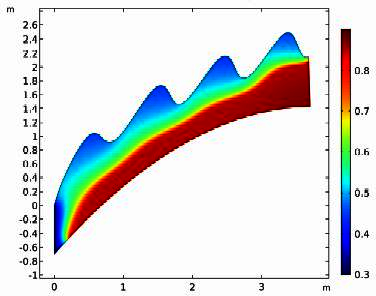
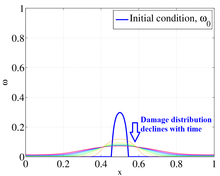
Finite Element Solution of Nonlinear Transient Rock Damage with Application in Geomechanics of Oil and Gas Reservoirs
The increasing energy demand calls for advances in technology which translate into more accurate and complex simulations of physical problems. Understanding the rock damage is essential to understanding the geomechanics of hydrocarbon reservoirs. The fragile microstructure of some ... 詳細を見る
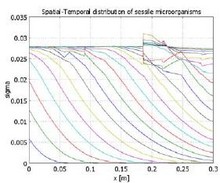
Transport, Growth, Decay and Sorption of Microorganisms and Nutrients through Porous Media: A Simulation with COMSOL
Transport of microorganisms through porous media governs many phenomena in bioremediation of environmental pollution problems and microbial enhanced oil recovery. The aim of this work is to investigate the effects of some transport parameters on breakthrough curves as well as on spatial ... 詳細を見る
Exergy Analysis of Polymer Flooding in Clastic Reservoirs
Using a 1-D model of polymer displacement, we analyze the exergy (maximum attainable work) balance of viscosifi ed water, e.g. with Arabic gum. The 1-D model shows the principle how such an analysis can be done. A comparison as to the displacement efficiency is made between three ... 詳細を見る
COMSOL numerical simulation of Differential Acoustic Resonance Spectroscopy
Differential Acoustic Resonance Spectroscopy (DARS) was developed to examine changes in the resonant frequencies of a cavity perturbed by the introduction of a centimetre-sized sample. This laboratory-based measurement technique fills an experimental gap between the low-frequency stress ... 詳細を見る
Integration of the DeProF Model for Two-Phase Flow in P.M. into the Subsurface Flow Module
Relative permeability maps for steady-state two-phase flow in porous media, delivered by implementing the DeProF model [1] algorithm, were integrated within COMSOL Multiphysics® software [2] to resolve field-scale flows in porous media. The mechanistic model DeProF [1], predicts the ... 詳細を見る
Two-phase Flow Calculations in Pore Unit Cells Implementing Mixed FEM/Lattice-Boltzmann Simulators
In general, macroscopic two-phase flow in porous media is a mixture of connected and disconnected oil flow. The latter is expressed as ganglion dynamics and drop traffic flow, patterns observed experimentally in pore network models [1,2] and real porous media [3,4]. This characteristic ... 詳細を見る
Pore-Level Influence of Contact Angle on Fluid Displacements in Porous Media
Wettability affects two-phase displacements in porous media by determining the microscopic distribution of fluids in pore spaces. The impact of wettability on transport properties at macro-scales has been widely addressed in literature; however a deeper understanding of wettability ... 詳細を見る