Silicon–Graphite-Blended Electrode with Thermodynamic Voltage Hysteresis
Application ID: 116001
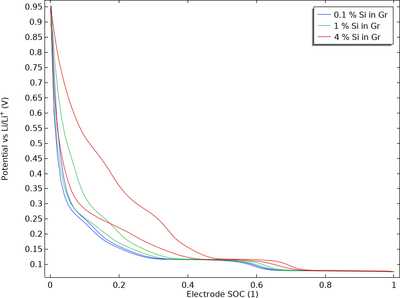
Due to its high capacity, silicon (Si) is often added to graphite in the negative electrode of lithium-ion batteries.
Silicon–graphite blended electrodes may exhibit significant thermodynamic voltage hysteresis (“path dependence”) because the equilibrium potential of the lithium–silicon intercalation reaction is dependent on the charge–discharge history of the electrode.
This model example demonstrates how to add Si as an Additional Electrode Material to a Porous Electrode in the Lithium-Ion Battery interface and how to define a memory variable capable of handling the voltage hysteresis using an additional Coefficient Form PDE interface.
この model の例は, 通常次の製品を使用して構築されるこのタイプのアプリケーションを示しています.
ただし, これを完全に定義およびモデル化するには, 追加の製品が必要になる場合があります. さらに, この例は, 次の製品の組み合わせのコンポーネントを使用して定義およびモデル化することもできます.
アプリケーションのモデリングに必要な COMSOL® 製品の組み合わせは, 境界条件, 材料特性, フィジックスインターフェース, パーツライブラリなど, いくつかの要因によって異なります. 特定の機能が複数の製品に共通している場合もあります. お客様のモデリングニーズに適した製品の組み合わせを決定するために, 製品仕様一覧 を確認し, 無償のトライアルライセンスをご利用ください. COMSOL セールスおよびサポートチームでは, この件に関するご質問にお答えしています.
