研究開発におけるマルチフィジックスシミュレーションの具体例
さまざまな業界のエンジニア, 研究者, 科学者がマルチフィジックスシミュレーションを使用して革新的な製品の設計とプロセスを研究および開発しています. COMSOL カンファレンスで発表したテクニカルペーパーやプレゼンテーションからインスピレーションを得てください. 以下の選択項目を参照するか, クイック検索ツールを使用して特定のプレゼンテーションを検索するか, アプリケーション領域でフィルタリングします.
COMSOL Conference 2024 論文集を見る
A lot of techniques are developed to treat soils polluted by hydrocarbons pollutants: incineration, thermal treatment, extraction, chemical oxidation, bioremediation… Some of these techniques are very energy consuming (incineration, thermal treatment…) and often need a subsequent ... 詳細を見る
The geomechanical effects related to CO2 injection into the Krechba formation at In Salah, Algeria, are considered through a coupled modeling approach to simulate simultaneously CO2 migration in the aquifer and the surrounding formations, as well as the poro-elastic stress changes ... 詳細を見る
In the study, we present an efficient absorbing boundary domain technique whose main application is the 3D finite element (FE) modelling of the so-called controlled-source electromagnetic (CSEM) data, collected for the geophysical exploration. The developed technique is based on the real ... 詳細を見る
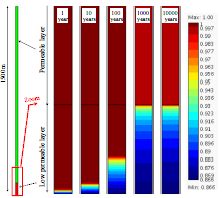
Bentonite clay is used as a protecting barrier around both the copper capsules in deposition holes and in deposition tunnels in the KBS-3 final disposal concept for spent nuclear fuel. The performance of these bentonite barriers will be investigated both experimentally and by modelling. ... 詳細を見る
This paper presents preliminary estimations of CO2 overpressure into the reservoir and CO2 leakage through the caprock and the overburden. A simple, two-phase flow model in porous media based on Darcy’s law was used, in order to explore easily long time periods. The models produced by ... 詳細を見る
We use 3D numerical models to analyze the ground deformation observed at Long Valley Caldera (LVC) between 1992 and 2000 via space-based geodetic techniques. More specifically, we implement a complex model that includes the topography and the material heterogeneities information of LVC. ... 詳細を見る
This study investigates the feedback between fault slip and dike intrusions during the Mono-Inyo eruption sequence of ~1350 A.D. (Mono Basin, California). We perform an extensive validation of 3D finite element models, implemented in the Structural Mechanics module of COMSOL ... 詳細を見る
A mathematical model for the simulation of contaminant such as heavy metals removal from soils by electric fields was performed in a 2-D geometry using COMSOL Multiphysics. Electrokinetic phenomena is the result of the coupling between hydraulic and electrical potential gradients in ... 詳細を見る
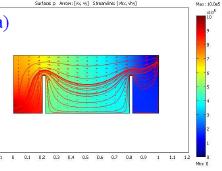
In this paper, an integrated model for ocean waves propagating over a submerged coastal structure, based on COMSOL Multiphysics, is presented. In the model, Navier-Stoke Equation is solved for the wave propagation and Biot’s poro-elastic model is solved for the porous seabed. The new ... 詳細を見る
A large amount of research work has been carried out in many countries to determine the viability of radioactive waste disposal in deep geological repositories. It is well known that excavation can cause damage around underground openings. On the other hand, the mechanical damage can ... 詳細を見る