研究開発におけるマルチフィジックスシミュレーションの具体例
さまざまな業界のエンジニア, 研究者, 科学者がマルチフィジックスシミュレーションを使用して革新的な製品の設計とプロセスを研究および開発しています. COMSOL カンファレンスで発表したテクニカルペーパーやプレゼンテーションからインスピレーションを得てください. 以下の選択項目を参照するか, クイック検索ツールを使用して特定のプレゼンテーションを検索するか, アプリケーション領域でフィルタリングします.
COMSOL Conference 2024 論文集を見る
The future development of electric vehicles is now strictly linked with their batteries. In parallel of the actual research focused on the development of new materials and increase their performances in terms of energy, power, cost, durability and weight, it is necessary to develop ... 詳細を見る
Individual batteries have their own operational temperature ranges, which shall be respected to avoid both damaging of the cells and shortening of the cycle life. In terms of the Li-Ion cells, many of them do not function well at higher temperatures. Therefore, a better understanding of ... 詳細を見る
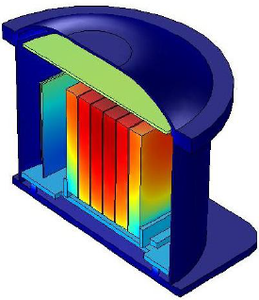
COMSOL Multiphysics was used to simulate the heat flux from battery cells via conjugate heat transfer physics which consist of laminar flow and heat transfer in solids and fluids. Laminar flow function was used to simulate natural convection of air within the sealed enclosure. Heat ... 詳細を見る
The ubiquitous commercial use of Lithium-Ion batteries (LIBs) has increased interest in their implementation into efficient energy storage systems for clean and renewable power sources and the electrical transportation industry. Unfortunately, LIBs are not yet technological mature to ... 詳細を見る
A design for the thermal management of the media used for packing Li-ion batteries used in hybrid and electric vehicles has been developed. The design satisfies all thermal and physical issues relating to the battery packs used in vehicles such as operating temperature range and volume, ... 詳細を見る
As the global use of COMSOL® apps continues to grow, many developers are seeking practical and secure methods to protect their applications and control their usage. While traditional paid software often relies on license keys, there has been a lack of simple and flexible tools tailored ... 詳細を見る
Failure of conventional lead-acid battery is attributed to degradation of solid active mass (PbO2 and PbSO4 ). A number of research efforts are underway worldwide to overcome degradation of active mass to improve the cycle life of lead-acid batteries. Soluble lead-acid flow battery ... 詳細を見る
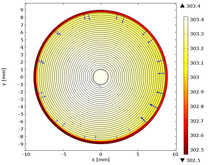
The characterization of Li-ion batteries is a relevant topic due to the recent developments in Electric Vehicles (EV’s) and Hybrid Electric Vehicles (HEV’s) applications. In order to manage these devices, accurate models are required. At NEXT ENERGY a two dimensional cell-level thermal ... 詳細を見る
Introduction: The drawbacks of most commercial “advanced battery” solutions are high price, danger, and low recyclability. The most cost efficient, environmental-friendly, and safest solutions so far is based on lead-acid electrochemistry, a proven technology for more than 150 years. Key ... 詳細を見る
Introduction: Recently, Li-ion battery is being widely used as power source for various applications from electronic gadgets to automotive industry. The performance and cycle life of Li-ion battery are becoming gradually important issues as the applications are shifting from small scale ... 詳細を見る