ミキサーモジュールアップデート
COMSOL Multiphysics® バージョン 6.4 では, ミキサーモジュールを利用のユーザー向けに, 回転ドメインモデリングのための効率的な代替機能, 高度な乱流モデルの初期条件の改善などが導入されています. これらのアップデートの詳細は以下をご覧ください.
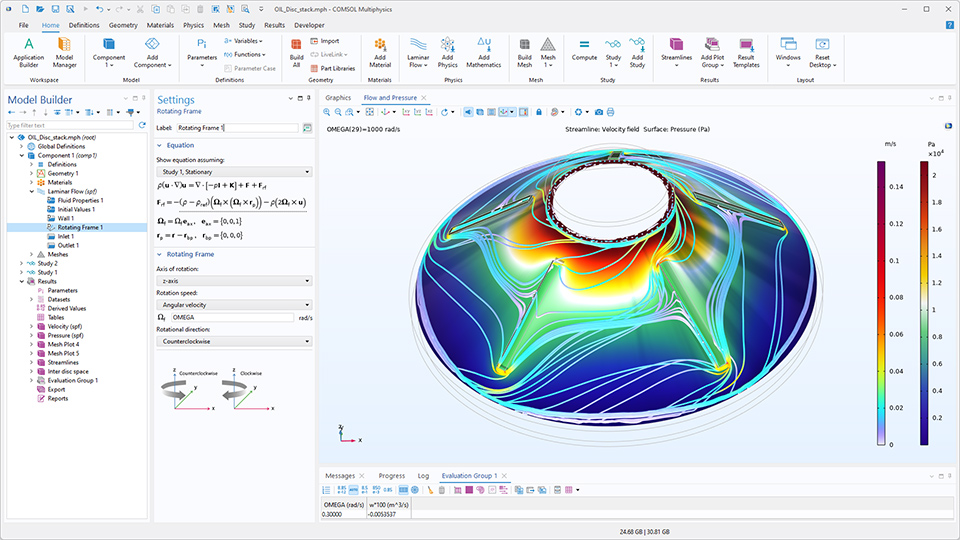
回転座標系機能:回転領域の代替
新しい 回転座標系 機能は, 定常または時間依存の回転座標系に対する流体流れ方程式を表現するため, 方程式を追加する必要がなく, 回転ドメインの低コストな代替手段となります. また, 換算圧力定式化の使用や, 遠心力に対する静水圧近似の組み込みといったオプションも用意されています.
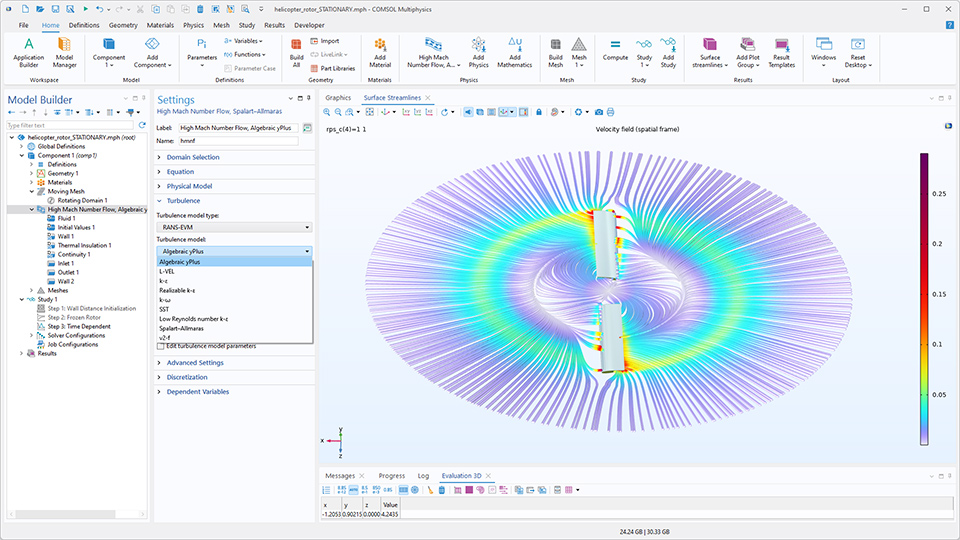
回転機械における高マッハ数流れのための代数的乱流モデル
回転機械における高マッハ数流れに, L-VEL および 代数的 yPlus 乱流モデルが利用可能になりました. これらの代数モデルは主に, より高度な乱流モデルの最適な初期条件を生成するために使用され, 収束性を向上させます. 例えばターボ機械のシミュレーションなど, 時間依存シミュレーションのより良い開始点を提供します.
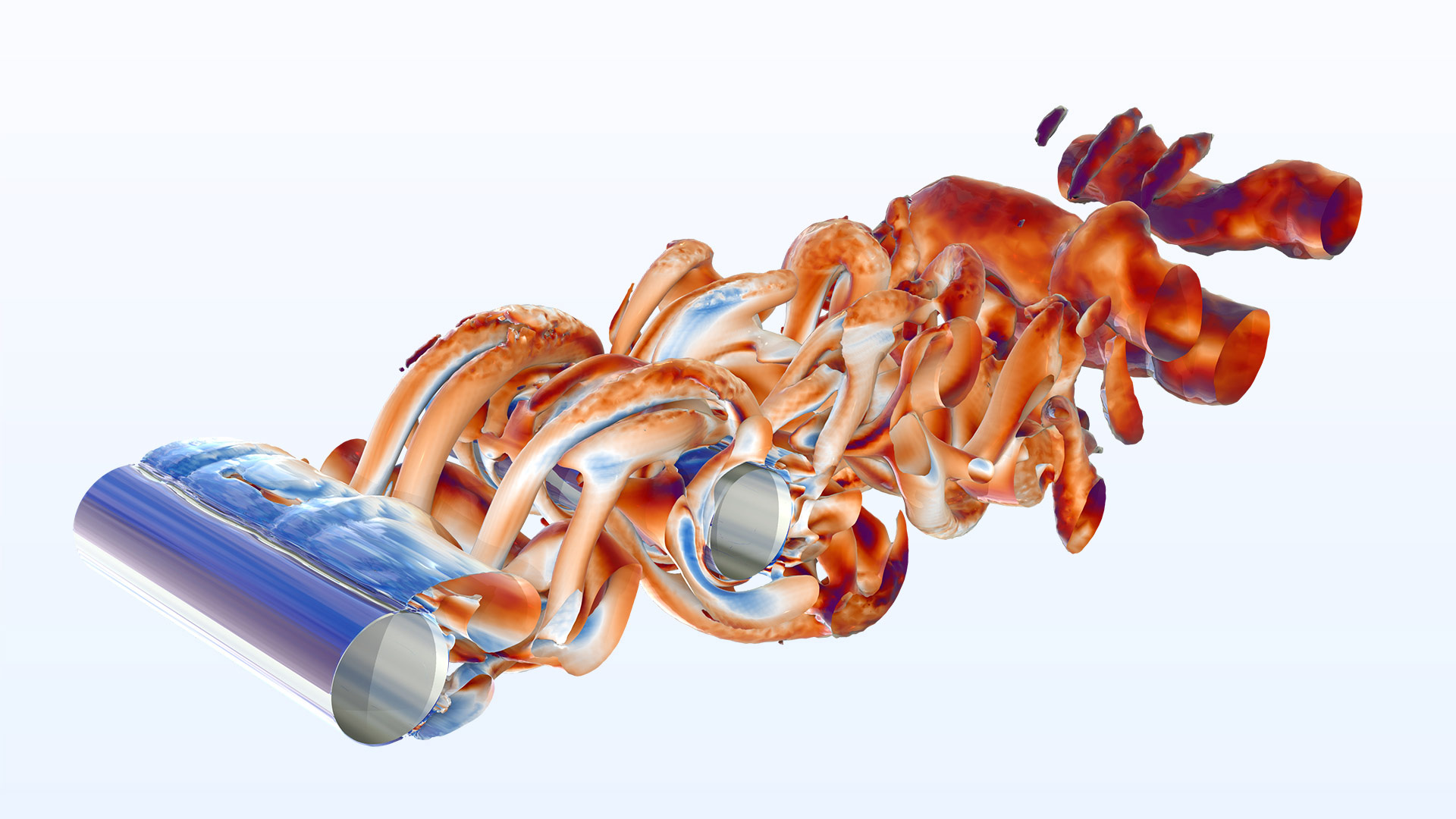
スケールアダプティブ非定常乱流シミュレーション
乱流 (SST) インターフェースは, フォン・カルマン長さスケールを乱流モデルに組み込むことで, スケールアダプティブシミュレーション (SAS) をサポートするようになりました. このアプローチにより, より広範囲の乱流スケールを解析し, 非常に詳細な流れ場が得られます. SAS は, 流体構造連成, 反応流, 非等温流れ, 流体騒音といったマルチフィジックスの分野に適用でき, より正確で洞察に富んだ結果をもたらします.
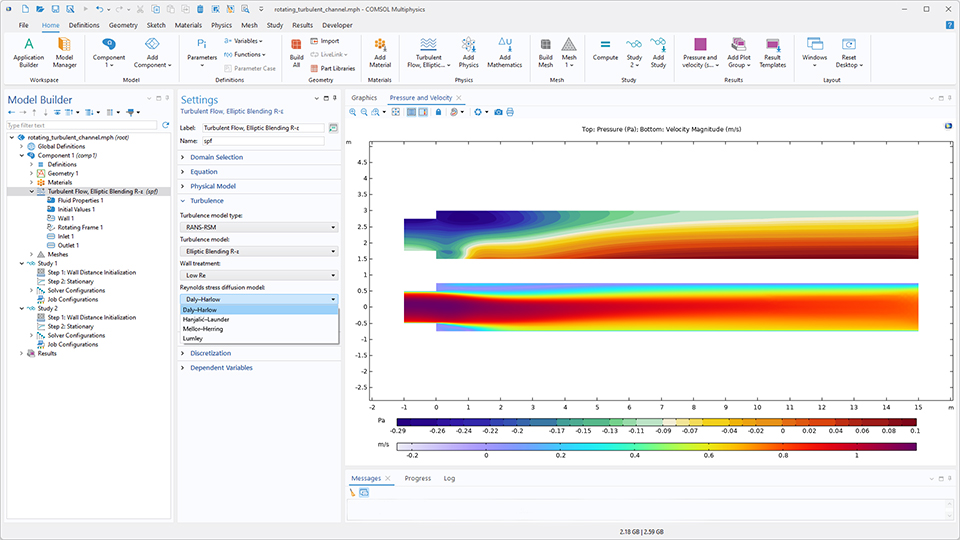
壁近傍処理を改良した乱流 (楕円ブレンディング R-ε) モデル
新しい 乱流 (楕円ブレンディング R-ε) モデルは, 壁近傍領域の圧力–ひずみ相関式および乱流粘性散逸率式をバルク領域とブレンドすることで, 壁近傍のレイノルズ応力について, 他の部分の挙動を損なうことなく正確な結果を提供します.