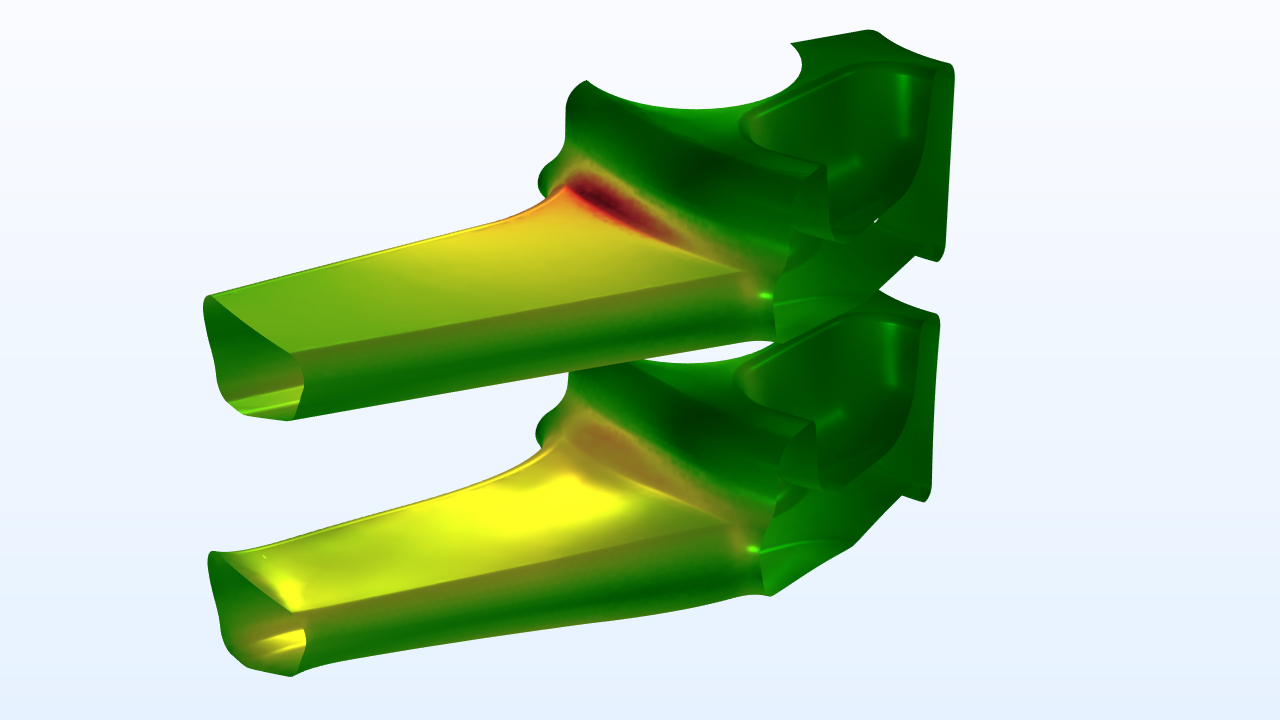
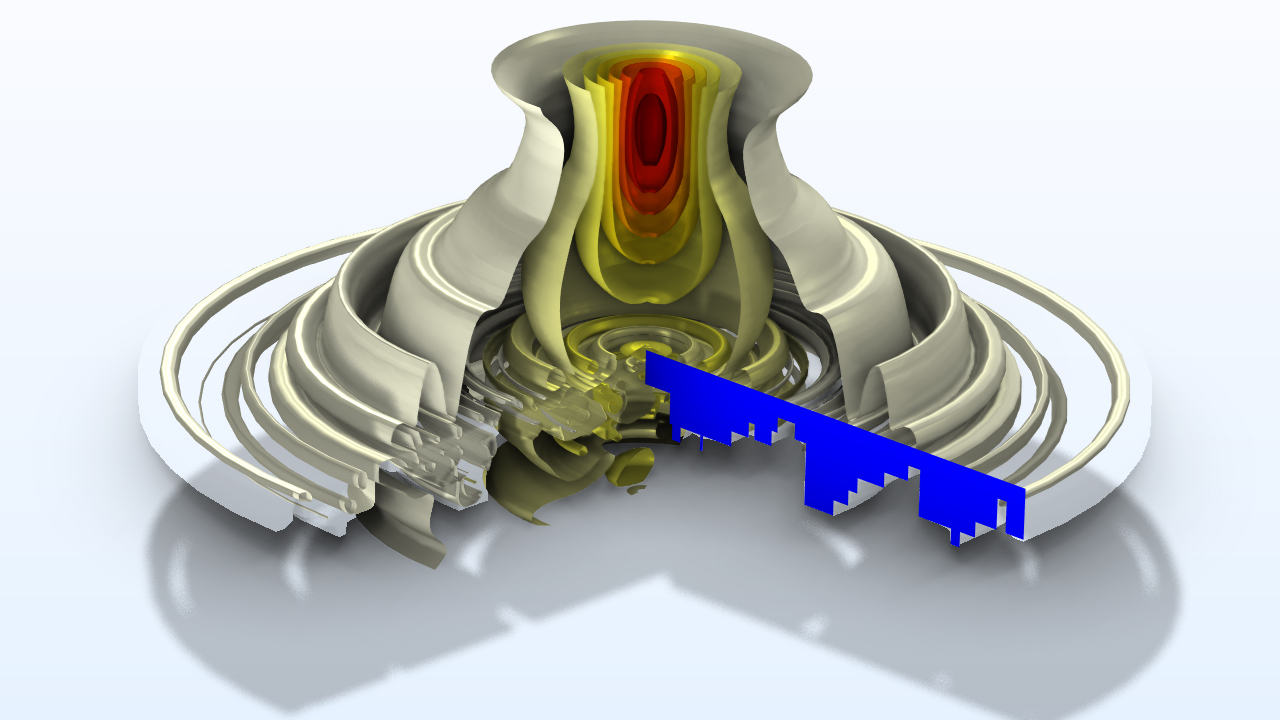
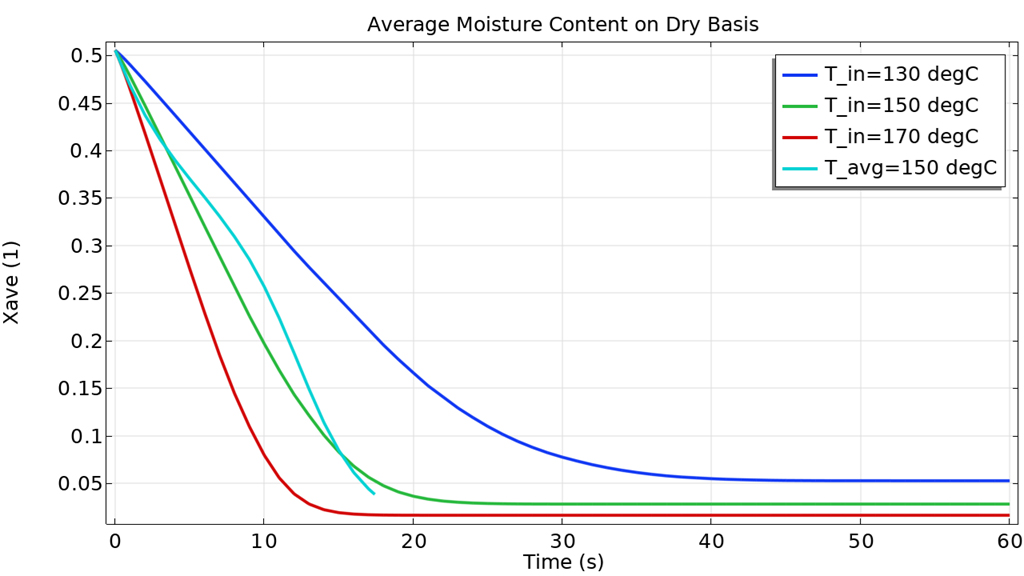
最適化モジュールアップデート
COMSOL Multiphysics® バージョン 6.4では, 最適化モジュールをご利用のユーザー向けに, 時間依存最適化の停止条件, パラメーター最適化スタディステップ, そしていくつかの新しいチュートリアルモデルが導入されています. これらのアップデートとその他の情報については, 以下をご覧ください.
時間依存最適化
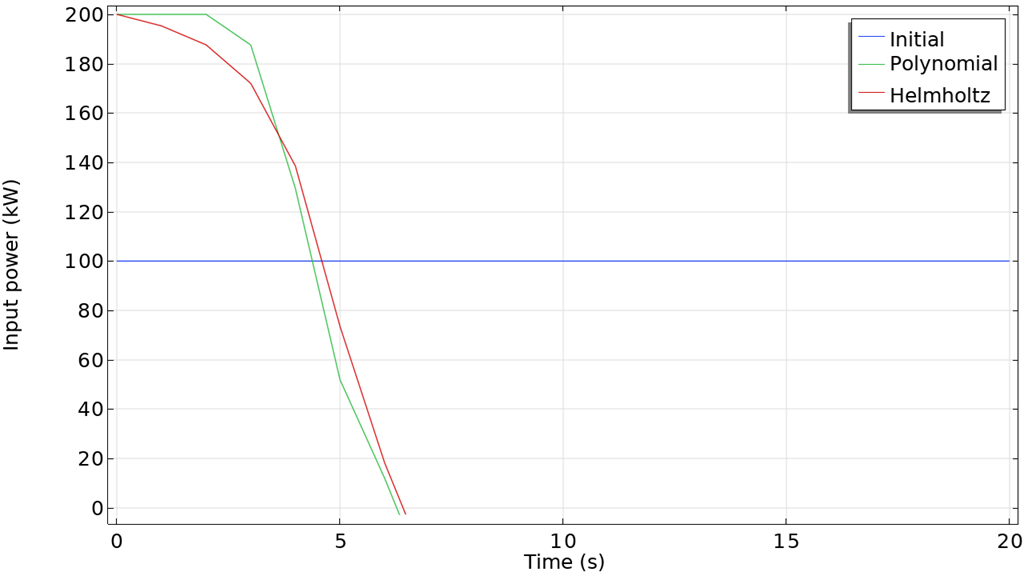
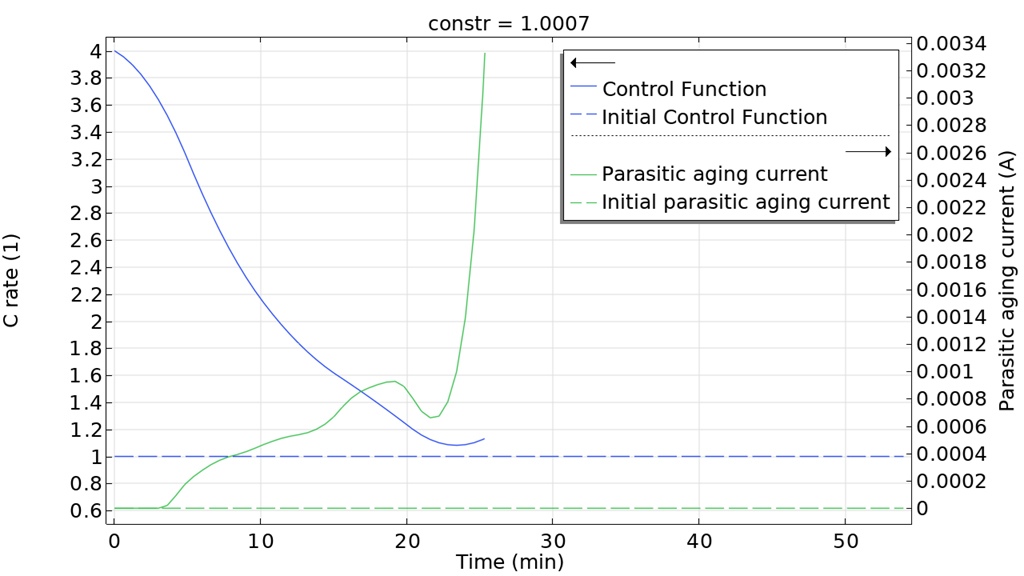
時間依存問題に対する勾配ベース最適化を, 最終時間の最適化にも使用できるようになりました. これにより, プロセスにかかる時間を最小化することも, ソルバーに最良の目的関数値を与える時間を選択させることもできます. 以下の例では, リチウムイオン電池の充電時間を最小化することを目標としています. このモデルでは 制御関数 機能が使用されており, 最適化結果を解析的関数または補間関数としてエクスポートできるようになりました.
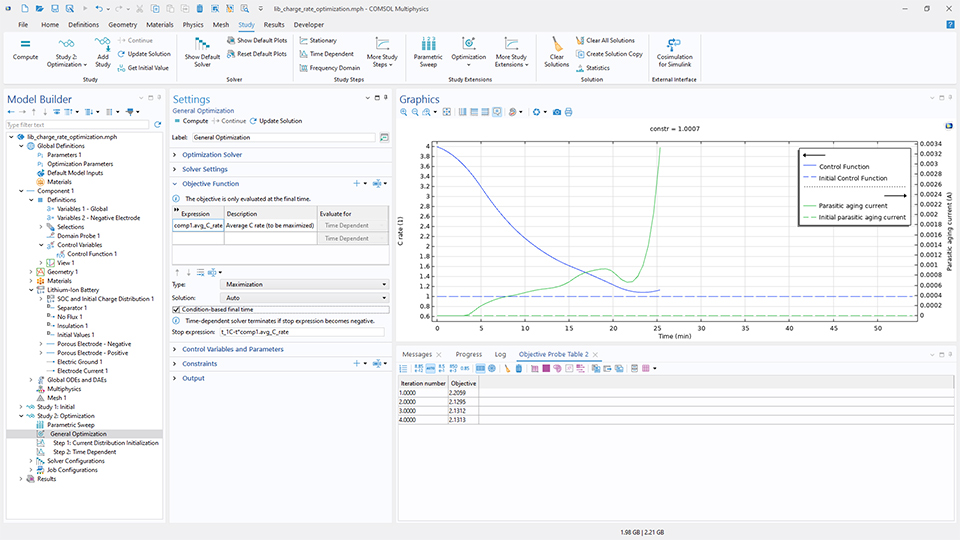
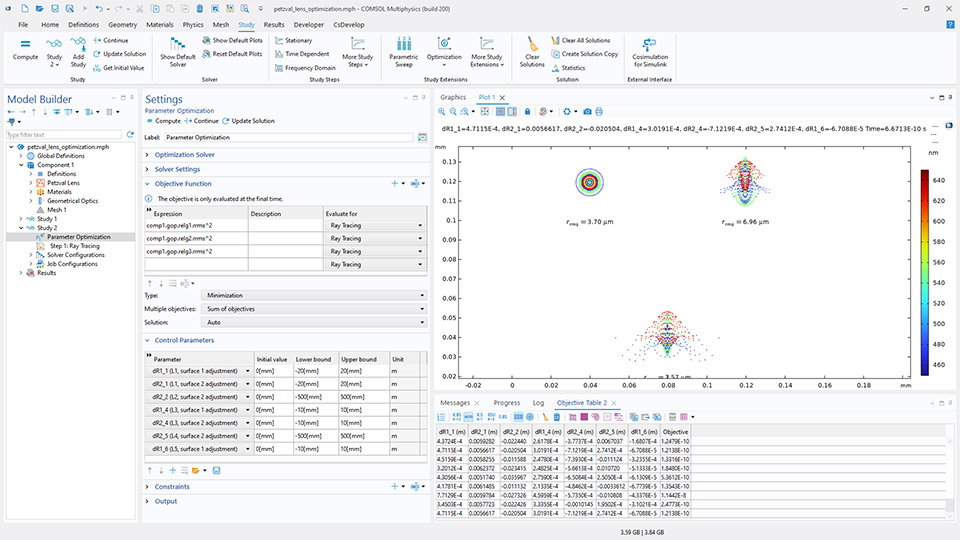
パラメーター最適化
勾配フリー最適化のために特別に設計された パラメーター最適化 スタディステップが導入されました. このステップでは, 制御変数のスケールが上下限に基づいて設定されるため, 手動での定義が不要になります. また, この機能は, 最適化されたパラメータに基づいて新しいパラメータケースを自動的に作成する機能も備えています.
さらに, ユーザーインターフェースが従来の 最適化 スタディステップ (一般最適化 に名称変更) と比較して再編成されました. 一般最適化 スタディステップと パラメーター最適化 スタディステップはどちらも有界なグローバル制御変数の初期値のランダム化をサポートし, 異なる局所最小値を特定できるようになりました.
勾配ベース最適化ソルバー
SNOPT 最適化ソルバーは廃止されました. 古いモデルは IPOPT に移行され, IPOPT が二次収束を達成するための推奨方法となっています (パラメーター推定は除く. パラメーター推定では Levenberg–Marquardt ソルバーの方が優れていると予想されます). また, 最適化スタディステップで MMA オプションを選択すると, 以前は (デフォルトのソルバー設定にて) GCMMA が使用されていましたが, 現在はスタディレベルで MMA と GCMMA の両方が利用可能になりました.
その他の新機能と改善点
- 新しい Pノルム と 標準偏差 機能:
- Pノルム 機能は, 構造問題における応力制約によく使用される場の最大値を近似する方法であり, 勾配ベースの最適化と互換性のある方法となっています.
- 標準偏差 機能を使用すると, 選択範囲にわたって場を均一化できます.
- 勾配ベースの最適化と互換性のある遠方場演算子が 電磁波 インターフェースに追加されました.
- 固有値の最適化では, 目的関数の式に非解析的演算子の使用がサポートされるようになり, 実数部のみを考慮して目標の固有周波数を設計できるようになりました.
- 密度モデル 機能に押出し制約のサポートが追加されました.
- 勾配ベースの最適化のパフォーマンスが向上しました.
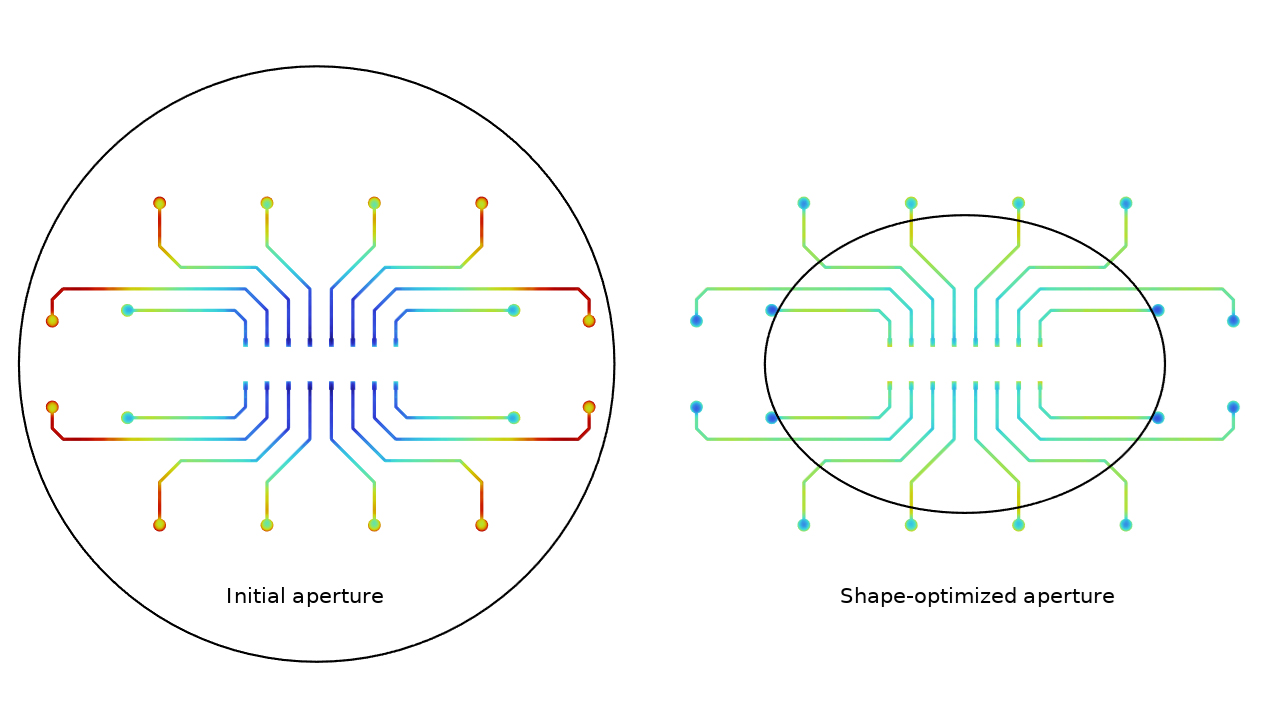
新規および更新されたチュートリアルモデル
COMSOL Multiphysics® バージョン 6.4 では, 最適化モジュールにいくつかの新規および更新されたチュートリアルモデルが追加されました.