パイプ流れモジュールアップデート
COMSOL Multiphysics® バージョン 6.4 では, パイプ流れモジュールを利用のユーザー向けに, 流れの制御と制限のシミュレーションのための新機能に加え, パイプネットワーク内の濃度プロファイルのシミュレーションや, パイプシステムを体積ドメインに接続するための拡張機能が導入されています. これらのアップデートの詳細については, 以下をご覧ください.
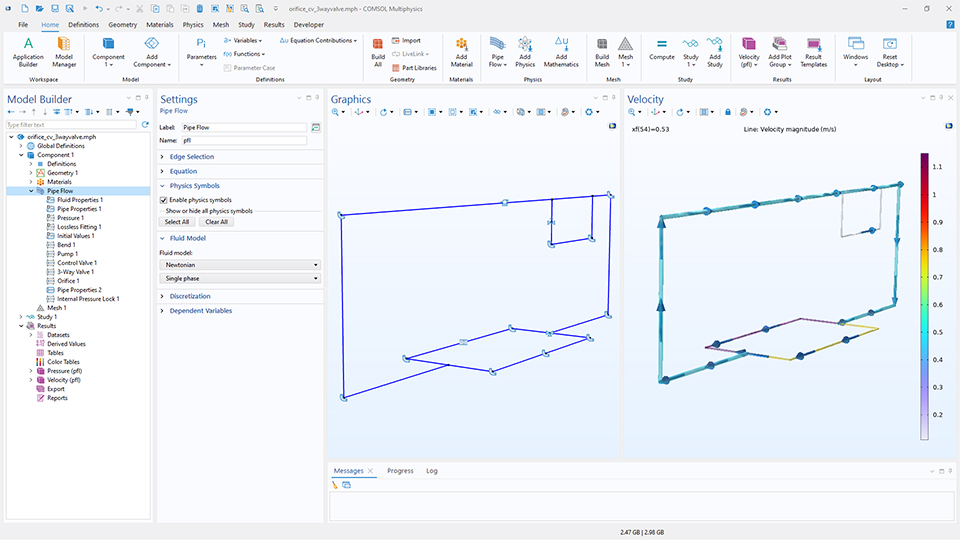
オリフィス, 制御弁, 3方弁機能による流量制御のモデル化
3つの新機能により, パイプ流れ インターフェースが拡張され, パイプネットワークをより柔軟にモデル化できるようになりました. オリフィス 機能は, 鋭い開口部と丸開口部の両方からの圧力降下を捉え, 流量制限を正確に表現します. 制御弁 機能は, 損失係数または産業標準の流量係数 (Cv または Kv) を使用して, 調整弁をシミュレートします. 3方弁 機能は, 3本のパイプが接続されたネットワークにおける流れの混合と分岐, および損失係数 Cv または Kv を使用したパラメーター化をサポートします. バルブ機能により, 異なる開度特性を持つ調整弁のシミュレーションが可能になり, 幅広い種類のバルブを表現できます.
新しいジャンクションおよびパイプ開口端機能
配管網における濃度プロファイルのシミュレーション機能が, 2つの新機能によって拡張されました. ジャンクション ノードは, 3本以上のパイプが接続された継手における物質移動を捉えます. パイプ開口端 ノードは, 指定された濃度で, パイプをタンクやリザーバーなどの外部システムに接続します. どちらの機能も可逆流れをサポートしており, 境界条件を流れの方向に合わせて自動的に調整することで, よりリアルで柔軟なシミュレーションを実現します.
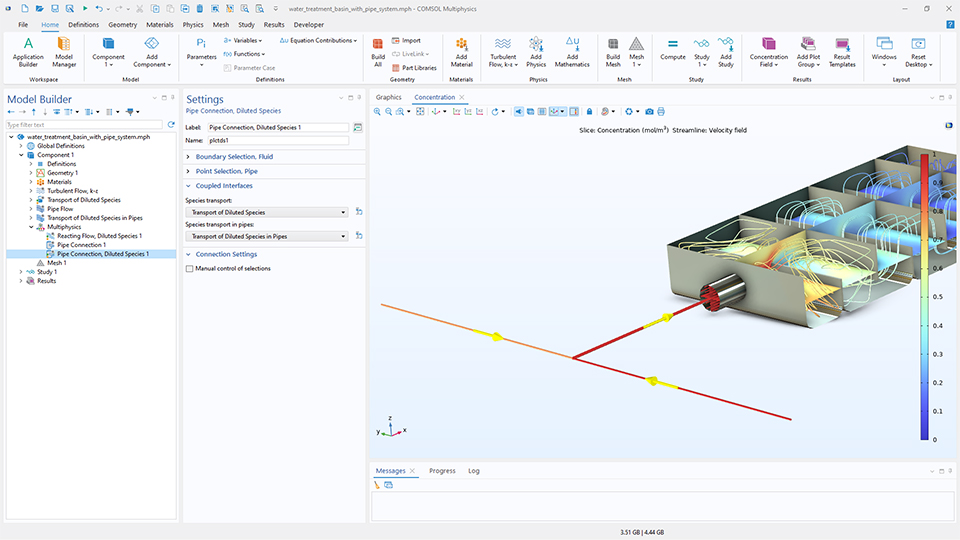
パイプ接続 (希釈種) カップリング
新しい パイプ接続 (希釈種) マルチフィジックスカップリングにより, パイプシステムと体積ドメインの接続が大幅に容易になりました. このカップリングは, 希釈種輸送 (パイプ) インターフェースでモデル化された 1D パイプセグメントを, 希釈種輸送 インターフェースでモデル化された体積領域にリンクします. このカップリングは, 境界を越えた正確な物質移動を正確に表現し, 可逆流れにも対応しており, 流れの方向に合わせて境界条件を自動的に調整します.
チュートリアルモデルの更新
COMSOL Multiphysics® バージョン 6.4 では, パイプ流れモジュールのチュートリアルモデルが更新されました.