Thermophoresis
Application ID: 12617
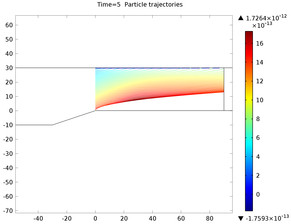
When a temperature gradient in a gas exists, suspended particles will tend to move from regions of high temperature to low. The force which produces this effect is called the thermophoretic force. Gas molecules colliding with a particle from the hot side have a higher velocity than the cold side, which results in a net force towards cold areas. This effect can be exploited to create thermal precipitators which can filter out undesirable particles from a feed gas. It can also be used in chemical vapor deposition, to inhibit the arrival of particle contaminants on the surface of a susceptor. This model simulates the size of a particle-free zone above a heated susceptor for different temperature gradients.
This model requires the Particle Tracing Module and the Heat Transfer Modules.
この model の例は, 通常次の製品を使用して構築されるこのタイプのアプリケーションを示しています.
ただし, これを完全に定義およびモデル化するには, 追加の製品が必要になる場合があります. さらに, この例は, 次の製品の組み合わせのコンポーネントを使用して定義およびモデル化することもできます.
- COMSOL Multiphysics® and
- 伝熱モジュール and
- 粒子追跡モジュール and
- either the CFD モジュール, マイクロフルイディクスモジュール, or プラズマモジュール
アプリケーションのモデリングに必要な COMSOL® 製品の組み合わせは, 境界条件, 材料特性, フィジックスインターフェース, パーツライブラリなど, いくつかの要因によって異なります. 特定の機能が複数の製品に共通している場合もあります. お客様のモデリングニーズに適した製品の組み合わせを決定するために, 製品仕様一覧 を確認し, 無償のトライアルライセンスをご利用ください. COMSOL セールスおよびサポートチームでは, この件に関するご質問にお答えしています.
