Wire Electrode
Application ID: 3471
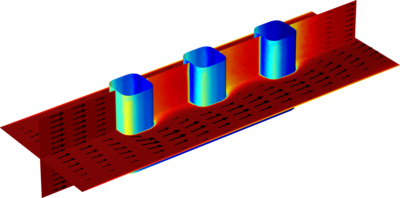
The electrochemical cell shown in this model can be regarded as a unit cell of a larger wire-mesh electrode that is common in many industrial processes. One of the most important aspects in the design of electrochemical cells is the current density distributions in the electrolyte and electrodes. Non-uniform current density distributions can be detrimental for the operation of electrochemical processes. In many cases, the parts of an electrode that are subjected to a high current density can degrade at a faster rate. Knowledge of the current density distribution is necessary to optimize the utilization of the electrocatalysts that are typically comprised of expensive noble metals. Non-uniform deposition and consumption, unnecessarily high overvoltages, energy losses and possible unwanted side-reactions represent effects that should be minimized. This example simulates the primary, secondary, and tertiary current density distributions of an arbitrary electrochemical cell with wire electrodes. The current density distributions are investigated in succession so as to also demonstrate good working practices by gradually introducing complexity when modeling electrochemical cells.
この model の例は, 通常次の製品を使用して構築されるこのタイプのアプリケーションを示しています.
ただし, これを完全に定義およびモデル化するには, 追加の製品が必要になる場合があります. さらに, この例は, 次の製品の組み合わせのコンポーネントを使用して定義およびモデル化することもできます.
- COMSOL Multiphysics® and
- either the バッテリデザインモジュール, 腐食解析モジュール, 電気化学モジュール, 電気めっきモジュール, or 燃料電池&電解槽モジュール
アプリケーションのモデリングに必要な COMSOL® 製品の組み合わせは, 境界条件, 材料特性, フィジックスインターフェース, パーツライブラリなど, いくつかの要因によって異なります. 特定の機能が複数の製品に共通している場合もあります. お客様のモデリングニーズに適した製品の組み合わせを決定するために, 製品仕様一覧 を確認し, 無償のトライアルライセンスをご利用ください. COMSOL セールスおよびサポートチームでは, この件に関するご質問にお答えしています.
