研究開発におけるマルチフィジックスシミュレーションの具体例
さまざまな業界のエンジニア, 研究者, 科学者がマルチフィジックスシミュレーションを使用して革新的な製品の設計とプロセスを研究および開発しています. COMSOL カンファレンスで発表したテクニカルペーパーやプレゼンテーションからインスピレーションを得てください. 以下の選択項目を参照するか, クイック検索ツールを使用して特定のプレゼンテーションを検索するか, アプリケーション領域でフィルタリングします.
COMSOL Conference 2024 論文集を見る
One of the crucial topics in this century is sustainable energy. In this respect, the exploitation of geothermal energy from deep hot aquifers becomes opportune. Hence, insight is required in the heat balance of potential aquifer systems. Essential issues are convection, conduction and ... 詳細を見る
Radionuclide transport modeling is a part of the research concerning geological disposal of spent nuclear fuel. Typically, the transport models near a single deposition hole focus on the reactions of nuclides, while the model geometry and the flow of groundwater are often simplified. In ... 詳細を見る
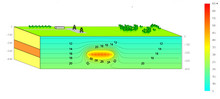
Green house gases emission associated with natural hazard of underground coal seam fire has been recognized as a worldwide problem leading to global warming threat. Therefore, in this paper a model to study underground coal fire is presented and the results will be devoted to strategic ... 詳細を見る
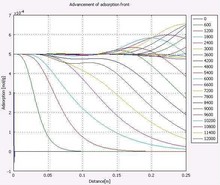
Numerical simulations of the equation of transport were performed using an adsorption isotherm equation, and a simple cubic polynomial. The 1D COMSOL implementation included solutes being injected from one face of a homogeneous, isotropic core (small sample of reservoir rock); where the ... 詳細を見る
New geothermal energy sources hold promise for the future. Deep submarine geothermal energy related to hydrothermal vents is emerging in many places along the oceanic spreading centers. Shallow submarine geothermal systems are found near to continental platforms. We present the initial ... 詳細を見る
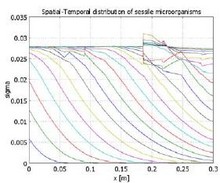
Transport of microorganisms through porous media governs many phenomena in bioremediation of environmental pollution problems and microbial enhanced oil recovery. The aim of this work is to investigate the effects of some transport parameters on breakthrough curves as well as on spatial ... 詳細を見る
We present the results of full-waveform time-dependent finite-element modelling of coupled seismoelectromagnetic wave propagation in fluid-saturated porous media. To describe the seismoelectric response of the system a new set of equations is developed which couple the poroelasticity ... 詳細を見る
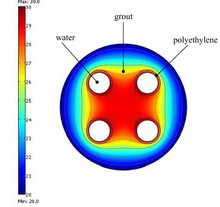
The results of two thermal response tests recently performed on two vertical borehole heat exchangers (BHEs) are presented. The BHEs have the same cross section and a depth of 100 m and 120 m respectively. The evaluation of the thermal properties of the ground and grout are performed by ... 詳細を見る
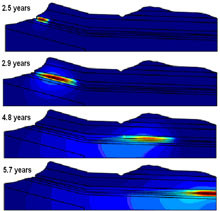
Disposal in deep clay geological formations is one of the promising options for disposal of high-level radioactive waste. Yet, they can generate considerable amounts of heat as a side effect of radioactive decay. This paper shows how COMSOL Multiphysics has been used to evaluate the ... 詳細を見る
An estimation method, known as Thermal Response Test, of the soil thermal properties necessary to the design of a borehole geothermal energy storage system is discussed in relation to its application to the ground having non–homogeneous composition. The governing equations of the ... 詳細を見る