Internal Short Circuit in a Lithium-Ion Battery
Application ID: 34891
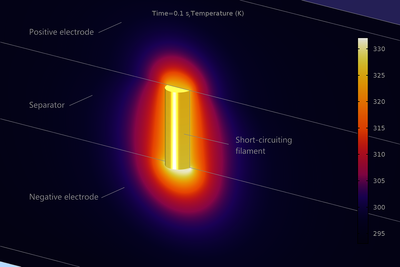
During an internal short circuit of a battery, the two electrode materials are internally and electronically interconnected, giving rise to high local current densities. Internal short circuits may occur in a lithium-ion battery due to, for instance, lithium dendrite formation or a compressive shock. A prolonged internal short circuit results in self discharge in combination with a local temperature increase. The latter effect is important because the electrolyte may start to decompose by exothermic reactions if the temperature reaches above a certain threshold, causing thermal runaway with potential health and safety hazards.
This tutorial model investigates the local temperature rise due to the occurrence of a penetrating metallic filament in the separator between the two porous electrode materials. The physics are set up using the Lithium-Ion Battery interface coupled to the Heat Transfer interface. The battery chemistry consists of a graphite negative electrode and an NMC positive electrode with an LiPF6 electrolyte.
この model の例は, 通常次の製品を使用して構築されるこのタイプのアプリケーションを示しています.
ただし, これを完全に定義およびモデル化するには, 追加の製品が必要になる場合があります. さらに, この例は, 次の製品の組み合わせのコンポーネントを使用して定義およびモデル化することもできます.
アプリケーションのモデリングに必要な COMSOL® 製品の組み合わせは, 境界条件, 材料特性, フィジックスインターフェース, パーツライブラリなど, いくつかの要因によって異なります. 特定の機能が複数の製品に共通している場合もあります. お客様のモデリングニーズに適した製品の組み合わせを決定するために, 製品仕様一覧 を確認し, 無償のトライアルライセンスをご利用ください. COMSOL セールスおよびサポートチームでは, この件に関するご質問にお答えしています.



