Lithium-Ion Battery Internal Resistance
Application ID: 19131
This tutorial digs deeper into the investigation of rate capability in a battery and shows how the Lithium-Ion Battery interface is an excellent modeling tool for doing this.
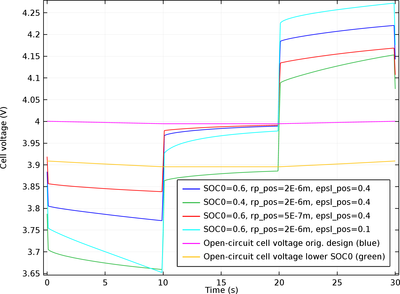
The rate capability is studied in terms of polarization (voltage loss) or the internal resistance causing this loss. A typical high current pulse test, namely a Hybrid Pulse Power Characterization (HPPC) test, is simulated here for this purpose. Primarily, the first 10 s of discharge and the subsequent relaxation at 298.15 K are investigated.
The Lithium-Ion Battery interface takes into account many physical battery properties of which some can be pinned down as design parameters directly affecting rate capability. These are:
Properties that decrease the internal resistance are normally thin battery domains, high porosities, and small active material particles.
A battery with the opposite design features has high internal resistance, but can instead store a lot capacity (energy) due to large active material particles and thick packed electrodes.
この model の例は, 通常次の製品を使用して構築されるこのタイプのアプリケーションを示しています.
ただし, これを完全に定義およびモデル化するには, 追加の製品が必要になる場合があります. さらに, この例は, 次の製品の組み合わせのコンポーネントを使用して定義およびモデル化することもできます.
アプリケーションのモデリングに必要な COMSOL® 製品の組み合わせは, 境界条件, 材料特性, フィジックスインターフェース, パーツライブラリなど, いくつかの要因によって異なります. 特定の機能が複数の製品に共通している場合もあります. お客様のモデリングニーズに適した製品の組み合わせを決定するために, 製品仕様一覧 を確認し, 無償のトライアルライセンスをご利用ください. COMSOL セールスおよびサポートチームでは, この件に関するご質問にお答えしています.



