Heat Transfer in Crossflow Heat Exchangers for Application with Microreactors
This paper explores methods of improving the heat transfer coefficient in a crossflow heat exchanger as would be employed in conjunction with an experimental or production microreactor.
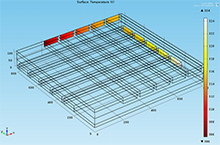
This derivation of the Cross-Flow Heat Exchanger from the COMSOL Multiphysics® software Model Library modifies the substrate geometry by adding two additional layers and uses the material copper in certain regions instead of stainless steel. Figure 1 shows the geometry of this set of models.
The incorporation of copper layers into the center of the crossflow heat exchanger geometry increased the heat transfer coefficient of the model by a factor of approximately 26.
Conclusion: The rate of heat transfer in this crossflow heat exchanger is significantly increased through structural and materials design modification.
ダウンロード
- pryor_presentation.pdf - 8.34MB
- pryor_poster.pdf - 1.76MB
- pryor_paper.pdf - 1.69MB
- pryor_abstract.pdf - 0.43MB



