Inertial Focusing Between Two Parallel Walls
Application ID: 42951
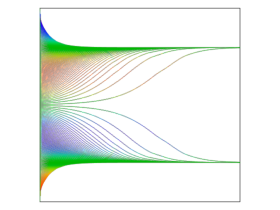
For more than 50 years, it has been known that neutrally buoyant particles in a flow channel tend to converge to specific locations in the channel cross section. For a cylindrical pipe, or two parallel planes carrying a Poiseuille flow, the equilibrium position is about 0.6 times the pipe radius, or a distance from parallel walls of about 0.2 times the channel width, respectively. This is called the Segre-Silberberg effect, while a ring of particles with a radius of 0.6 times the pipe radius is sometimes called the Segre-Silberberg annulus.
In this benchmark model, we reproduce the case of a flow channel bounded by two parallel walls. Wall-dependent lift and drag forces are exerted on the neutrally buoyant particles as they are carried along the channel by a parabolic fluid velocity profile. As particles are carried through the channel, the inertial lift force causes them to reach equilibrium positions at distances from the center of 0.3 D, where D is the distance between the walls. These equilibrium positions are consistent with the Segre-Silberberg effect.
この model の例は, 通常次の製品を使用して構築されるこのタイプのアプリケーションを示しています.
ただし, これを完全に定義およびモデル化するには, 追加の製品が必要になる場合があります. さらに, この例は, 次の製品の組み合わせのコンポーネントを使用して定義およびモデル化することもできます.
アプリケーションのモデリングに必要な COMSOL® 製品の組み合わせは, 境界条件, 材料特性, フィジックスインターフェース, パーツライブラリなど, いくつかの要因によって異なります. 特定の機能が複数の製品に共通している場合もあります. お客様のモデリングニーズに適した製品の組み合わせを決定するために, 製品仕様一覧 を確認し, 無償のトライアルライセンスをご利用ください. COMSOL セールスおよびサポートチームでは, この件に関するご質問にお答えしています.
