Monopile with Dissolving Sacrificial Anodes
Application ID: 36071
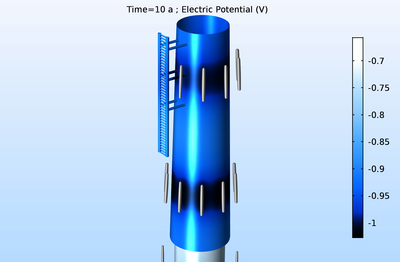
A monopile foundation is a large-diameter structural element that can be used to support structures like offshore wind turbines. This application exemplifies how the cathodic protection of a monopile decreases over time as the sacrificial anodes dissolve. The model can be used to evaluate secondary current distribution electrode kinetics on the protected steel structure by taking into account the simultaneous electrochemical reactions that lead to metal dissolution and oxygen reduction (mixed potential).
The monopile geometry consists of an upper component with a coated steel surface and a lower uncoated steel pipe. It is also surrounded by either seawater or mud, with differing Tafel expression reaction kinetics used for these different environments. The tutorial model is solved using a time-dependent study for a time period of 12 years. Two cases are investigated: when the whole monopile is grounded, and when the transition piece is grounded and the lower pipe is connected to the transition piece through a lumped resistance.
The model also uses the new customized Sacrificial Edge Anode subnode for modeling slender sacrificial anodes along geometric edges, which is now available in the Secondary Current Distribution interface. The subnode enables you to model the changing cathodic protection properties of the anodes as they dissolve in time-dependent simulations.
この model の例は, 通常次の製品を使用して構築されるこのタイプのアプリケーションを示しています.
ただし, これを完全に定義およびモデル化するには, 追加の製品が必要になる場合があります. さらに, この例は, 次の製品の組み合わせのコンポーネントを使用して定義およびモデル化することもできます.
アプリケーションのモデリングに必要な COMSOL® 製品の組み合わせは, 境界条件, 材料特性, フィジックスインターフェース, パーツライブラリなど, いくつかの要因によって異なります. 特定の機能が複数の製品に共通している場合もあります. お客様のモデリングニーズに適した製品の組み合わせを決定するために, 製品仕様一覧 を確認し, 無償のトライアルライセンスをご利用ください. COMSOL セールスおよびサポートチームでは, この件に関するご質問にお答えしています.



