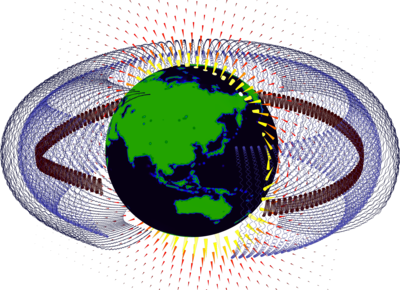
Motion of Trapped Protons in Earth's Magnetic Field
Application ID: 19047
This model demonstrates the path of relativistic protons within Earth's magnetic field.
Due to the dipole nature of Earth's magnetic field, charged particles, such as electrons and protons, can get trapped in stable configurations within it for long periods of time.
These configurations involve the particles rapidly bouncing from magnetic pole to magnetic pole, and drifting around the earth; this drifting motion is slow in comparison to the bounce motion. This forms belts of trapped radiation.
The magnetic field of the earth is not a perfect dipole and complex fits and empirical models exist to model the field in detail. In order to rapidly compute this magnetic field, an external function is used to encapsulate an implementation of the IGRF (International Geomagnetic Reference Field). This implementation is written in c and compiled into a shared library.
Ref: http://www.ngdc.noaa.gov/IAGA/vmod/igrf.html
この model の例は, 通常次の製品を使用して構築されるこのタイプのアプリケーションを示しています.
ただし, これを完全に定義およびモデル化するには, 追加の製品が必要になる場合があります. さらに, この例は, 次の製品の組み合わせのコンポーネントを使用して定義およびモデル化することもできます.
アプリケーションのモデリングに必要な COMSOL® 製品の組み合わせは, 境界条件, 材料特性, フィジックスインターフェース, パーツライブラリなど, いくつかの要因によって異なります. 特定の機能が複数の製品に共通している場合もあります. お客様のモデリングニーズに適した製品の組み合わせを決定するために, 製品仕様一覧 を確認し, 無償のトライアルライセンスをご利用ください. COMSOL セールスおよびサポートチームでは, この件に関するご質問にお答えしています.



