Squeeze-Film Gas Damping in an Accelerometer
Application ID: 1432
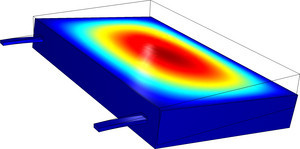
Squeezed-film gas damping is a critical aspect of many MEMS transducers and actuators. In accelerometers, for example, inertia produces a motion that the device detects. A typical structure connects a large proof mass to surrounding structures with elastic beams, which forms a mechanical oscillator with a specific resonance frequency. However, in accurate motion-detection applications these resonances are unwanted, and the device should dampen the movements to produce smooth time-step and frequency responses.
In this model, a narrow gap formed by two solid horizontal plates restricts the displacement of the gas perpendicular to the surfaces. When the sensor squeezes the gap, the gas flows out from its edges. The narrow pathway restricts the flow, which causes gas pressure to increase, which decelerates the plates’ movement.
This example show how the squeezed film gas damping can be coupled to the mechanical displacements in a microsystem accelerometer. Specifically it uses a modeling interface that couples the linearized Reynolds equation, to displacements in the sensor.
この model の例は, 通常次の製品を使用して構築されるこのタイプのアプリケーションを示しています.
ただし, これを完全に定義およびモデル化するには, 追加の製品が必要になる場合があります. さらに, この例は, 次の製品の組み合わせのコンポーネントを使用して定義およびモデル化することもできます.
- COMSOL Multiphysics® and
- either the CFD モジュール, MEMS モジュール, or 構造力学モジュール
アプリケーションのモデリングに必要な COMSOL® 製品の組み合わせは, 境界条件, 材料特性, フィジックスインターフェース, パーツライブラリなど, いくつかの要因によって異なります. 特定の機能が複数の製品に共通している場合もあります. お客様のモデリングニーズに適した製品の組み合わせを決定するために, 製品仕様一覧 を確認し, 無償のトライアルライセンスをご利用ください. COMSOL セールスおよびサポートチームでは, この件に関するご質問にお答えしています.



