Heating Circuit — Layered Shell Version
Application ID: 87231
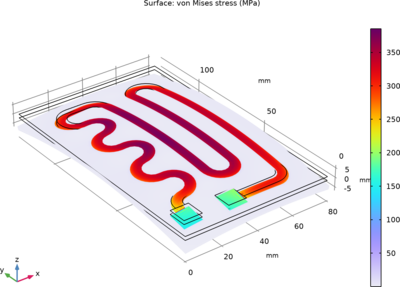
Small heating circuits find use in many applications. For example, in manufacturing processes, they heat up reactive fluids. The device in this tutorial consists of an electrically resistive layer deposited on a glass plate. The layer results in Joule heating when a voltage is applied to the circuit, which results in a structural deformation. The layer’s properties determine the amount of heat produced.
This multiphysics example simulates the electrical heat generation, heat transfer, and mechanical stresses and deformations of a heating circuit device. The model uses the Heat Transfer in Shells interface in combination with the Electric Currents in Layered Shells interface and the Layered Shell interface.
この model の例は, 通常次の製品を使用して構築されるこのタイプのアプリケーションを示しています.
ただし, これを完全に定義およびモデル化するには, 追加の製品が必要になる場合があります. さらに, この例は, 次の製品の組み合わせのコンポーネントを使用して定義およびモデル化することもできます.
- COMSOL Multiphysics® and
- 複合材料モジュール and
- 伝熱モジュール and
- either the AC/DC モジュール, or MEMS モジュール and
- either the MEMS モジュール, or 構造力学モジュール
アプリケーションのモデリングに必要な COMSOL® 製品の組み合わせは, 境界条件, 材料特性, フィジックスインターフェース, パーツライブラリなど, いくつかの要因によって異なります. 特定の機能が複数の製品に共通している場合もあります. お客様のモデリングニーズに適した製品の組み合わせを決定するために, 製品仕様一覧 を確認し, 無償のトライアルライセンスをご利用ください. COMSOL セールスおよびサポートチームでは, この件に関するご質問にお答えしています.



