分子流モジュール
自由分子流を理解し予測する
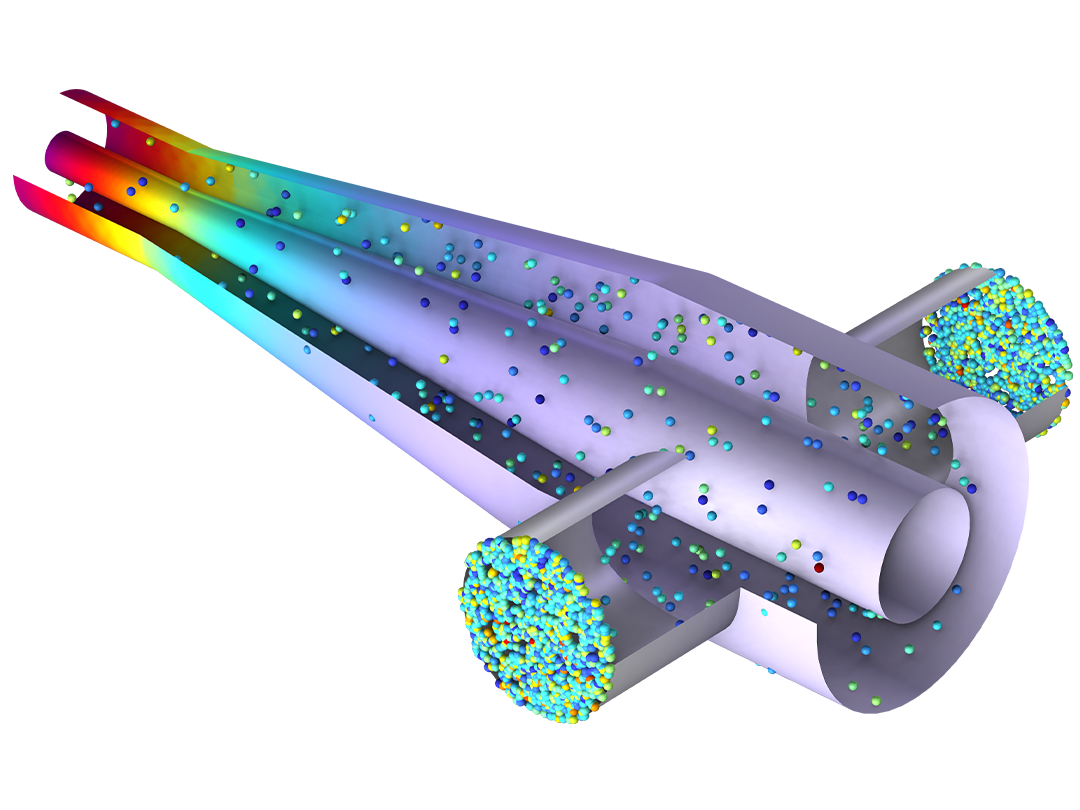
分子流モジュールは, 真空系を設計し, 自由分子流領域における低圧ガスの流れを理解および予測するために使用される COMSOL Multiphysics® ソフトウェアのアドオンです. 歴史的に, この領域の流れは直接シミュレーションであるモンテカルロ (DSMC) 法によってモデル化されてきました. DSMC 法は, 系を通じてランダム化された多数の粒子の軌道を計算しますが, モデリングプロセスに統計的ノイズが導入されるという欠点があります. 真空系で発生するような低速の流れの場合, DSMC によって導入されるノイズによりシミュレーションが実行不可能になります. 分子流モジュールは, この統計的ノイズがまったくない決定論的アプローチを使用し, 低速の流れをシミュレートするための高速で便利な方法を提供します.
COMSOL へお問い合わせ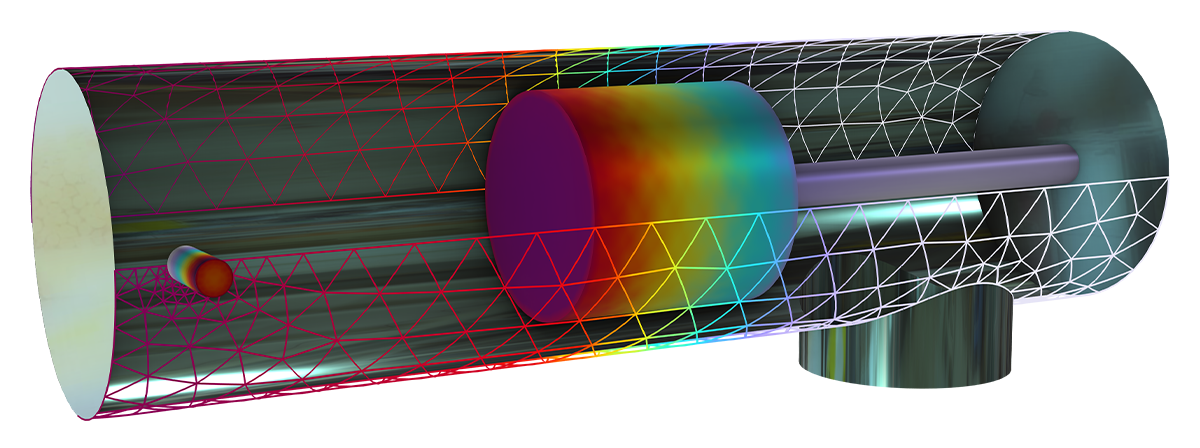
分子流モジュールの特徴と機能
分子流モジュールには, 自由分子流領域の流れを正確にシミュレートする機能が含まれています.
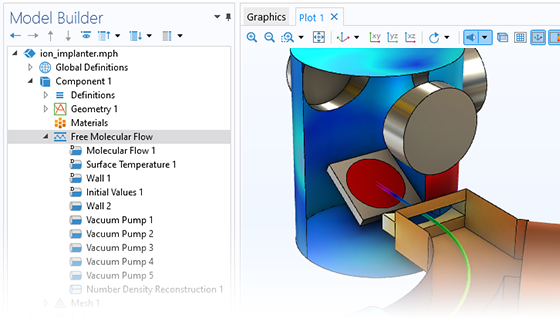
自由分子流
自由分子流インターフェースは, 高度に希薄化されたガス流れを正確にシミュレートします. このインターフェースは, ジオメトリの境界における分子流束を解像し, 境界における数密度, 圧力, および熱流束を計算するためのオプションを含みます. このインターフェースを使用すると, 境界上にのみメッシュを生成してシミュレーションを実行することができます. ドメイン内の数密度を再構築するために, ボリュームメッシュを簡単に追加できます. 自由分子流インターフェースを使用すると, 本物の CAD モデルをベースとして分子流シミュレーションを実行できます.
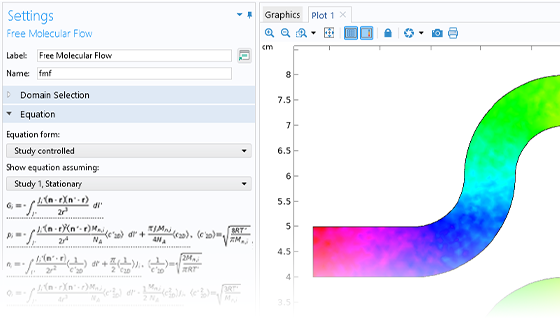
角度係数法
非常に希薄な流れの場合, 自由分子流インターフェースは角度係数法を使用します. これは決定論的なアプローチであり, 粒子ベースの方法よりも高速です. この方法は, 圧力と数密度を計算するための近似コンダクタンス方法よりもはるかに正確です. また, 複数種のガスを同時に簡単に扱うことができます.
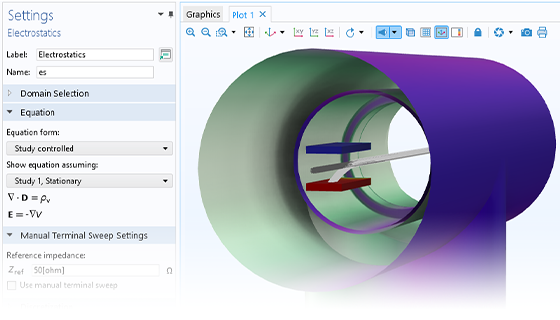
拡張マルチフィジックス解析
分子流モジュールは, COMSOL 製品の他のモジュールと組み合わせて, マルチフィジックスシミュレーションを実行する機能を拡張できます. モジュールを組み合わせることで, フィールド変数やパラメーターなどの他のモジュールからのデータを, インターフェースカップリングを介して分子流モジュールで使用できます. たとえば, 分子流モジュールと粒子追跡モジュールを組み合わせると, 背景数密度の計算に使用される 自由分子流インターフェースを荷電粒子追跡インターフェースと組み合わせて, 粒子と周囲の中性原子の間の衝突をシミュレートできます.
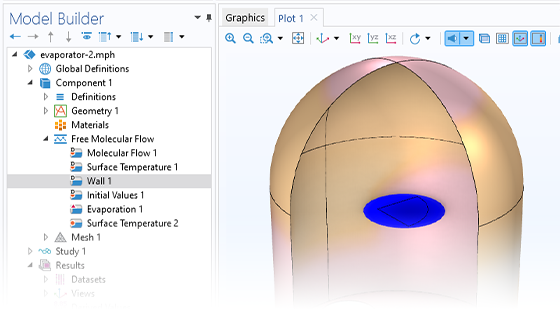
境界条件
分子流モジュールは, モデルに割り当てることができるさまざまな境界条件を提供します. 隣接する大きなリザーバーまたは完全な真空による境界上の圧力を指定するための機能が組み込まれています. 非等温分子流の表面温度を直接指定することも可能です. さらに, このモジュールは, ポンプ流量や吸着される分子の割合などのパラメーターを指定したり, 任意の表面での吸着速度を直接設定したりする機能を提供します. このモジュールは, 蒸着源をモデル化し, 数値または任意の式を使用して表面から放出される流束を指定する機能も提供します.
さらに, 分子流モジュールには, 真空系内のさまざまな種類の固体表面をモデル化するためのさまざまな境界条件が含まれています. たとえば, 入射分子が表面から拡散反射される壁機能を使用して境界を定義できます. また, 入射分子が拡散反射され, 追加の分子が拡散的にガス放出されるアウトガス壁機能を使用するオプションもあります. 吸脱着オプションを使用すると, 入射分子の一部が吸収され, 残りの分子が拡散反射されます. さらに, 堆積壁タイプオプションを使用して, 分子が堆積する表面をモデル化できます.
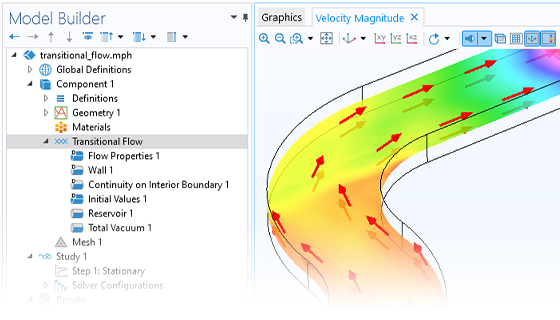
遷移流れ
分子流モジュールを使用すると, 自由分子流よりも希薄化がわずかに低いけれど, スリップ流れよりはさらに希薄化した流れをシミュレートできます. これには通常, ナビエ・ストークス限界から分子流量限界に及ぶ希薄な流れが含まれます. 遷移流インターフェースは, このようなタイプの希薄流用に特別に設計されており, 離散速度法に基づいています. このアプローチでは, 分子のすべての潜在的な速度を表すために有限の速度集合が選択されます. 次に, 原子がこれらの速度ビンに割り当てられ, インターフェースによって各ビンの数密度が計算されます. 対流方程式はドメイン内で求解され, ビン間で分子を再配置する散乱項によって補完されます. このモジュールには, 設定を効率化するためのさまざまな専用の境界条件も含まれています. 遷移流シミュレーションは計算負荷が高く, かなりの処理能力と時間を必要とするため, CAD ジオメトリモデルを簡素化できる場合に最適に適用できます.
シミュレーションのニーズはそれぞれ異なります.
COMSOL Multiphysics® ソフトウェアがお客様のご要望を満たすかどうかをきちんと評価するために, ぜひ当社までお問い合わせください. 営業担当者との打ち合わせを通じて, 各個人に向いたお勧めや文書化されたモデル事例などをお送りすることができ, 最大限の評価結果を引き出すことができます. 最終的にどのライセンスオプションがあなたの要望にとって最適かを選択することができます.
"COMSOL へお問い合わせ" ボタンをクリックしてください. あなたの連絡先情報およびご意見やご質問をご入力のうえ送信してください. 1営業日以内に営業担当者よりご連絡いたします.
次のステップ:
ソフトウェアデモをリクエスト